Should we wash chicken before cooking or not?
- Like
- Digg
- Del
- Tumblr
- VKontakte
- Buffer
- Love This
- Odnoklassniki
- Meneame
- Blogger
- Amazon
- Yahoo Mail
- Gmail
- AOL
- Newsvine
- HackerNews
- Evernote
- MySpace
- Mail.ru
- Viadeo
- Line
- Comments
- Yummly
- SMS
- Viber
- Telegram
- Subscribe
- Skype
- Facebook Messenger
- Kakao
- LiveJournal
- Yammer
- Edgar
- Fintel
- Mix
- Instapaper
- Copy Link
Posted: 5 April 2022 | Abi Sritharan (New Food) | No comments yet
Researchers have found that raw chicken can contaminate surfaces whether you wash it or not, so what should you do?
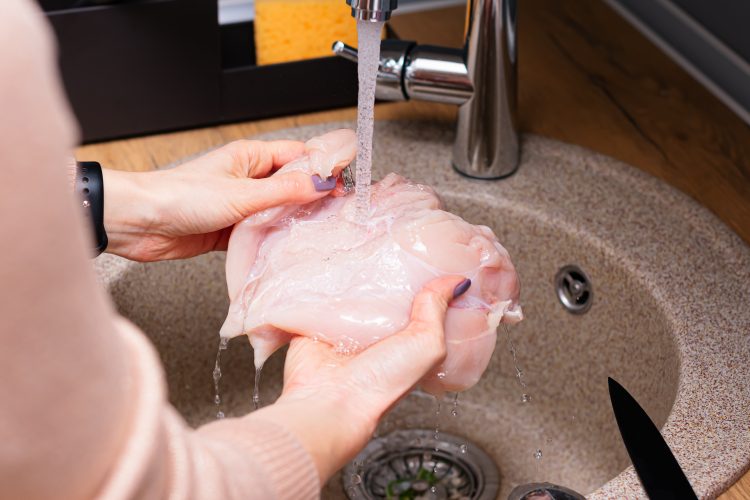


There are some food safety debates that people just can’t agree upon: is the expiry date needed? Do you have to throw out the whole loaf of bread if there is mould on one slice? Should we wash raw poultry before cooking it?
Washing raw poultry is not recommended, due to concerns about inadvertently contaminating other foods and surfaces and increasing the risk of foodborne illness.
A recent study – published in the Journal of Food Protection – aimed to assess the impact of washing poultry on kitchen contamination.
“We wanted to know what effect an educational intervention would have on getting people to stop washing poultry before cooking, and what effect any resulting change in behaviour might have on reducing contamination in the kitchen,” said Ellen Shumaker, one of the authors of the study. “We also wanted to get a better idea of how, if at all, washing poultry actually led to increased contamination in the kitchen.”
For the study – conducted by researchers from North Carolina State University – 300 home cooks who said they washed poultry before cooking it were recruited. The researchers sent food safety information to 142 of the study participants via email, outlining risk-reduction efforts, including the recommendation to not wash raw poultry during food preparation. The remaining 158 study participants did not receive the education intervention.
All 300 study participants were then invited to test kitchens equipped with video cameras that filmed participants preparing and cooking chicken thighs and a salad. After preparing the chicken thighs, but before putting the chicken in the oven, participants were called out of the kitchen to conduct a short interview. Participants were then sent back into the kitchen to cook the chicken thighs, prepare the salad, and clean the kitchen as they would at home.
You may also like:
What the study participants didn’t know was that the chicken thighs were injected with a harmless strain of bacteria, which the researchers would be able to detect. This allowed researchers to swab surfaces in the kitchen to see whether any cross-contamination occurred during the food preparation and cooking process.
When study participants left the kitchen to conduct the interview, researchers swabbed the kitchen to identify any potential contamination. This process was repeated after each participant had completed cooking the meal and cleaned the kitchen. The prepared salad was also tested for possible contamination.
The majority of the participants who received the intervention did not wash the chicken (96 percent), whilst only 39 percent of the participants who did not receive the intervention avoided washing their chicken.
However, according to the study, the researchers were surprised to see that people who did wash their chicken and people who didn’t wash their chicken had similar levels of contamination from the raw chicken in their prepared salads.
“We think the salad contamination stems from people doing a poor job of washing their hands after handling the raw chicken, and/or doing a poor job of sanitising the sink and surrounding surfaces before rinsing or handling the salad,” said Shumaker.
“Regardless of whether people washed their chicken, the kitchen sinks became contaminated by the raw chicken, while there was relatively little contamination of nearby counters. This was a little surprising, since the conventional wisdom had been that the risk associated with washing chicken was because water would splash off of the chicken and contaminate surrounding surfaces. Instead, the sink itself was becoming contaminated, even when the chicken wasn’t being washed.”
“Washing the chicken is still not a good idea, but this study demonstrates the need to focus on preventing contamination of sinks and emphasising the importance of hand-washing and cleaning and sanitising surfaces,” she added.
The experiment highlights the importance of handwashing, as well as cleaning and sanitising the kitchen in order to reduce the risk of foodborne illness when cooking.
Related topics
Contaminants, Food Safety, Hygiene, Pathogens, Research & development