“Outdated” UK pig ammonia emissions factors to be revised
- Like
- Digg
- Del
- Tumblr
- VKontakte
- Buffer
- Love This
- Odnoklassniki
- Meneame
- Blogger
- Amazon
- Yahoo Mail
- Gmail
- AOL
- Newsvine
- HackerNews
- Evernote
- MySpace
- Mail.ru
- Viadeo
- Line
- Comments
- Yummly
- SMS
- Viber
- Telegram
- Subscribe
- Skype
- Facebook Messenger
- Kakao
- LiveJournal
- Yammer
- Edgar
- Fintel
- Mix
- Instapaper
- Copy Link
Posted: 18 May 2020 | Sam Mehmet (New Food) | No comments yet
Pig ammonia emissions factors are said to based on studies 20 years old, and revising these factors aims to help compliant producers avoid unnecessary expenses.
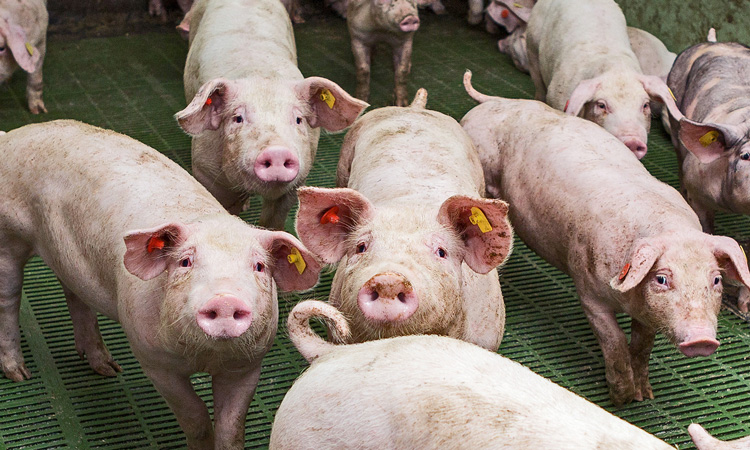


International agreements on air pollution have resulted in the UK farming industry being required to achieve a 16 percent reduction in ammonia emissions by 2030, but the pig ammonia emissions factors on which this will be based are from studies over 20 years old, according to the Agriculture and Horticulture Development Board (AHBD).
To redress these figures, AHBD’s Environment and Buildings team has announced that it has a large project underway to measure the ammonia emissions from different pig buildings in the UK.
The Environment Agency (EA) uses emissions factors (EFs) to assess the impact of permitted farms’ ammonia emissions on the environment and Natural England then uses this in ammonia dispersion modelling. Defra also uses them to estimate UK emissions of ammonia from pig production for annual reporting to the European Commission.
“In our initial trials, we measured ammonia emissions from one straw-based and one fully slatted finisher farm, focusing on ammonia concentration in the inlet and exhaust air, using a bespoke analyser,” said Zanita Markham, Environment and Buildings KT Officer.
“In addition, the number of pigs, weights, feed intake, protein content of diets, ventilation rates, external and internal temperature and relative humidity were also recorded, as per an internationally recognised, standardised protocol. This means that results from different studies can be compared and systems benchmarked.”
Data so far has reportedly suggested that EFs are generally lower than they were 20 years ago. The figures are an average of 1.72 kg of ammonia per animal place per year, compared with the current EF of 3.1 kg. For finishers on straw, it is an average 1.22 kg of ammonia per animal place per year, compared with the current EF of 2.97 kg.
This work is now being replicated across more sites and systems before the results can be applied more widely. This includes free-farrowing solid-floor systems, weaners on solid floor, finishers on solid floor, finishers on fully slatted floor, dry sows on solid floor, and straw-based finishers.
“These results have given us the confidence to develop an accelerated programme of monitoring so the industry can work from a better baseline,” Markham added.
The ammonia monitoring programme is expected to demonstrate that a lot of existing pig housing will already be compliant and, therefore, avoid unnecessary expense for producers, in time for the compliance deadline in February 2021.