Study says urban land could grow fruit and veg for 15 percent of population
- Like
- Digg
- Del
- Tumblr
- VKontakte
- Buffer
- Love This
- Odnoklassniki
- Meneame
- Blogger
- Amazon
- Yahoo Mail
- Gmail
- AOL
- Newsvine
- HackerNews
- Evernote
- MySpace
- Mail.ru
- Viadeo
- Line
- Comments
- Yummly
- SMS
- Viber
- Telegram
- Subscribe
- Skype
- Facebook Messenger
- Kakao
- LiveJournal
- Yammer
- Edgar
- Fintel
- Mix
- Instapaper
- Copy Link
Posted: 25 March 2020 | Sam Mehmet (New Food) | No comments yet
The researchers found that green spaces including parks, gardens, allotments, roadside verges and woodland cover 45 percent of Sheffield – a figure similar to other UK cities.
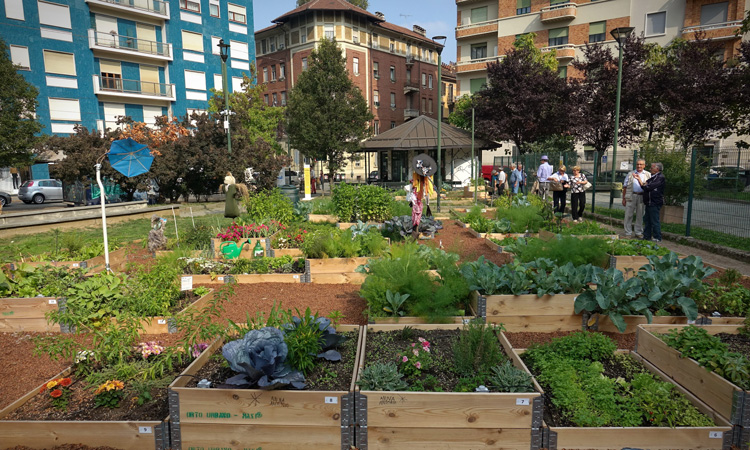


Growing fruit and vegetables in just 10 percent of a city’s gardens and other urban green spaces could provide 15 percent of the local population with their ‘five a day’, according to new research from the Institute for Sustainable Food at the University of Sheffield. The researchers investigated the potential for urban horticulture by mapping green spaces and grey spaces across the city.
The interdisciplinary team used data from Ordnance Survey and Google Earth to reveal that an extra 15 percent of the city’s green space, such as parks and roadside verges, also has potential to be converted into community gardens or allotments.
Putting domestic gardens, allotments and suitable urban public green spaces together would reportedly open up 98m2 per person in Sheffield for growing food. This equates to more than four times the 23m2 per person currently used for commercial horticulture across the UK.
According to the research, if 100 percent of this space was used for growing food, it could feed approximately 709,000 people per year their ‘five a day’, or 122 percent of the population of Sheffield. But even converting a more realistic 10 percent of domestic gardens and 10 percent of available green space, as well as maintaining current allotment land, could provide 15 percent of the local population – 87,375 people – with sufficient fruit and veg.
With just 16 percent of fruit and 53 per cent of vegetables sold in the UK grown domestically, such a move could significantly improve the nation’s food security, the researchers claimed.
The study also investigated the potential for soil-free farming on flat roofs using methods such as hydroponics, where plants are grown in a nutrient solution, and aquaponics, a system combining fish and plants. These techniques could allow year-round cultivation with minimal lighting requirements, using greenhouses powered by renewable energy and heat captured from buildings, with rainwater harvesting for irrigation.
Flat roofs were found to cover 32 hectares of land in Sheffield city centre. While equivalent to just 0.5m2 per person, the researchers believed that the high-yielding nature of soil-free farming means this could make a significant contribution to local horticulture.
The UK currently imports 86 percent of its total tomato supply – but if just 10 percent of the flat roofs identified within the centre of Sheffield became soil-free tomato farms, it would reportedly be possible to grow enough to feed more than eight percent of the population one of their ‘five a day’. This increases to more than 60 percent of people if three quarters of the flat roof area is utilised.
Related topics
Environment, Food Security, Research & development, Sustainability